This site uses cookies to provide you with a more responsive and personalized service. By clicking "Accept," you agree to the use of cookies on this site. Please read our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy for more information on the use of cookies on this website.
Frequent Monitoring
Frequent blood glucose monitoring is a critical component of daily management to help ensure glucose homeostasis and guide adjustments to cornstarch dosing and nutritional plans.1-3
Understand the daily demands of GSDIa management
Sample “Day in the Life” – Living with GSDIa
Meghan is a 31-year-old woman living with GSDIa. She has been managing her condition with a cornstarch regimen comprised of 6 doses and a strict nutrition plan recommended by her dietitian. Below is a sample schedule of a day in her life.
Disclaimer: Meghan is a fictitious patient. For illustrative purposes only. Patients should work with their care team to develop an appropriate plan that meets their unique needs. This sample schedule should not be provided to patients.
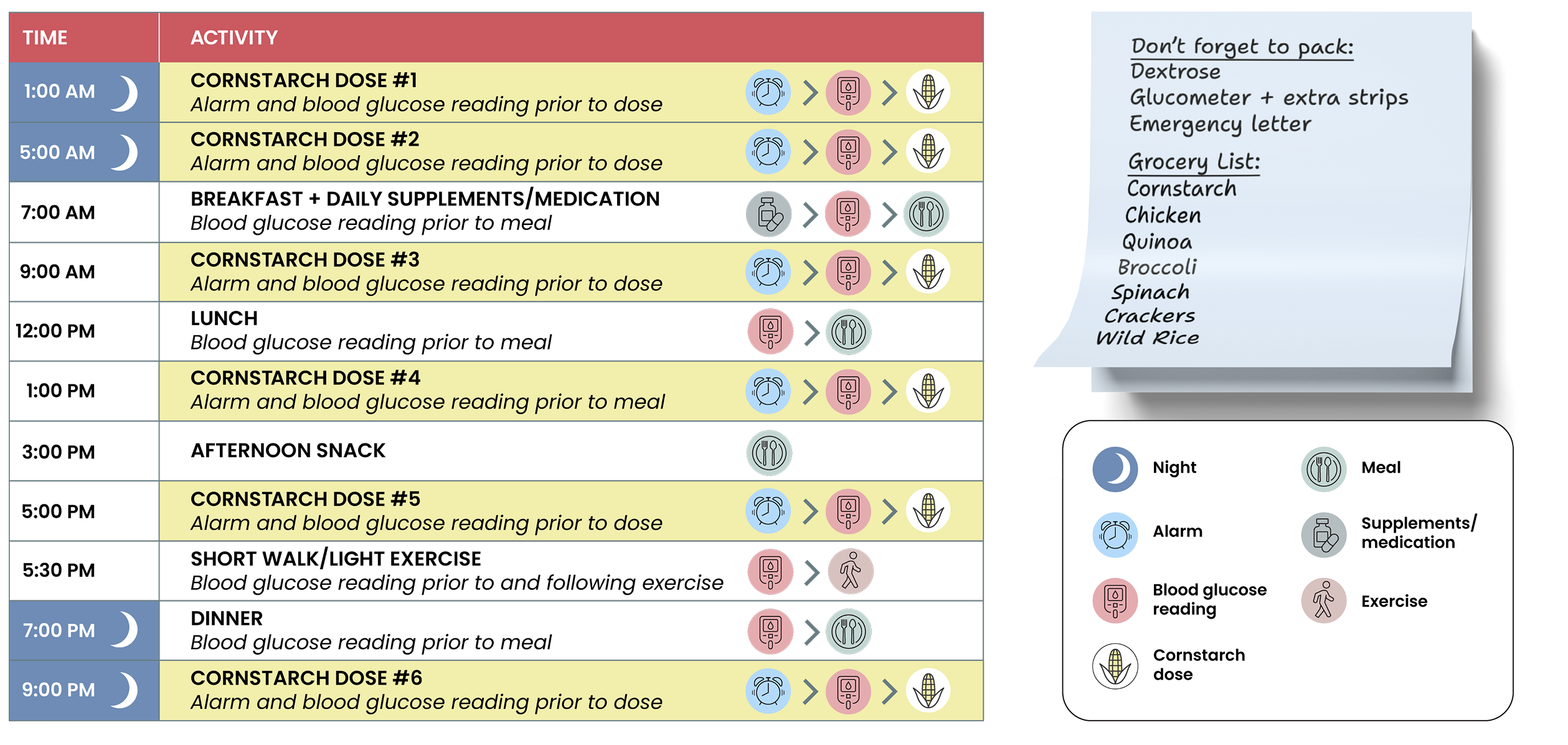

Abbreviation: GSDIa, glycogen storage disease type Ia.
References: 1. Kishnani PS, Austin SL, Abdenur JE, et al. Diagnosis
and management of glycogen storage disease type I: a practice guideline of the American College of Medical
Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med. 2014;16(11):e1. 2. Bali DS,
El-Gharbawy A, Austin S, et al. Glycogen storage disease type I. 2006. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM,
et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024.
Accessed June 27, 2025. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1312/ 3. Derks TGJ, Rodriguez-Buritica DF, Ahmad A, et al. Glycogen storage
disease type Ia: current management options, burden and unmet need. Nutrients. 2021;13(11):3828.