This site uses cookies to provide you with a more responsive and personalized service. By clicking "Accept," you agree to the use of cookies on this site. Please read our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy for more information on the use of cookies on this website.
Management of GSDIa relies on an around-the-clock cornstarch regimen and adherence to a nutrition plan1
To maintain glucose homeostasis, patients with GSDIa must avoid fasting and consume frequent cornstarch doses every few hours throughout the day and night.1 Strict adherence to the dosing schedule is vital, as even one skipped or delayed dose may result in life-threatening consequences of hypoglycemia, including seizures, neurologic damage, and death.1 Overfeeding with cornstarch due to fear of hypoglycemia can contribute to hyperglycemia and insulin resistance.1,2
Individuals with GSDIa consume large amounts of cornstarch daily1
All children and many adults must wake up during the night to consume cornstarch; one study indicates that more than 90% of adults with GSDIa awaken to consume cornstarch during the night3
I have to wake up every 4 hours in order to consume cornstarch, which disrupts my sleep, so I am constantly exhausted…
Dietary modifications are required to prevent metabolic abnormalities1
Individuals with GSDIa are unable to metabolize fructose or galactose and are often advised to avoid foods containing these sugars, as well as other sugars that break down into them (eg, sucrose, lactose).1 Avoidance of these simple sugars requires severely limiting or eliminating broad food groups such as fruit and dairy, further contributing to the risk of developing nutritional deficiencies.1
Daily supplementation with a sugar-free multivitamin, calcium, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids is often required to prevent nutritional deficiencies2
Example GSDIa caloric composition1,5
To potentially avoid nutritional deficiencies, may consider supplementing with:
- Sugar-free multivitamin
- Calcium
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Vitamin D
May be advised to limit or avoid foods containing:
- Fructose and galactose, as well as other sugars that break down into them (eg, sucrose, lactose)
- Added sugar, sorbitol, honey, maple syrup, molasses or high-fructose corn syrup
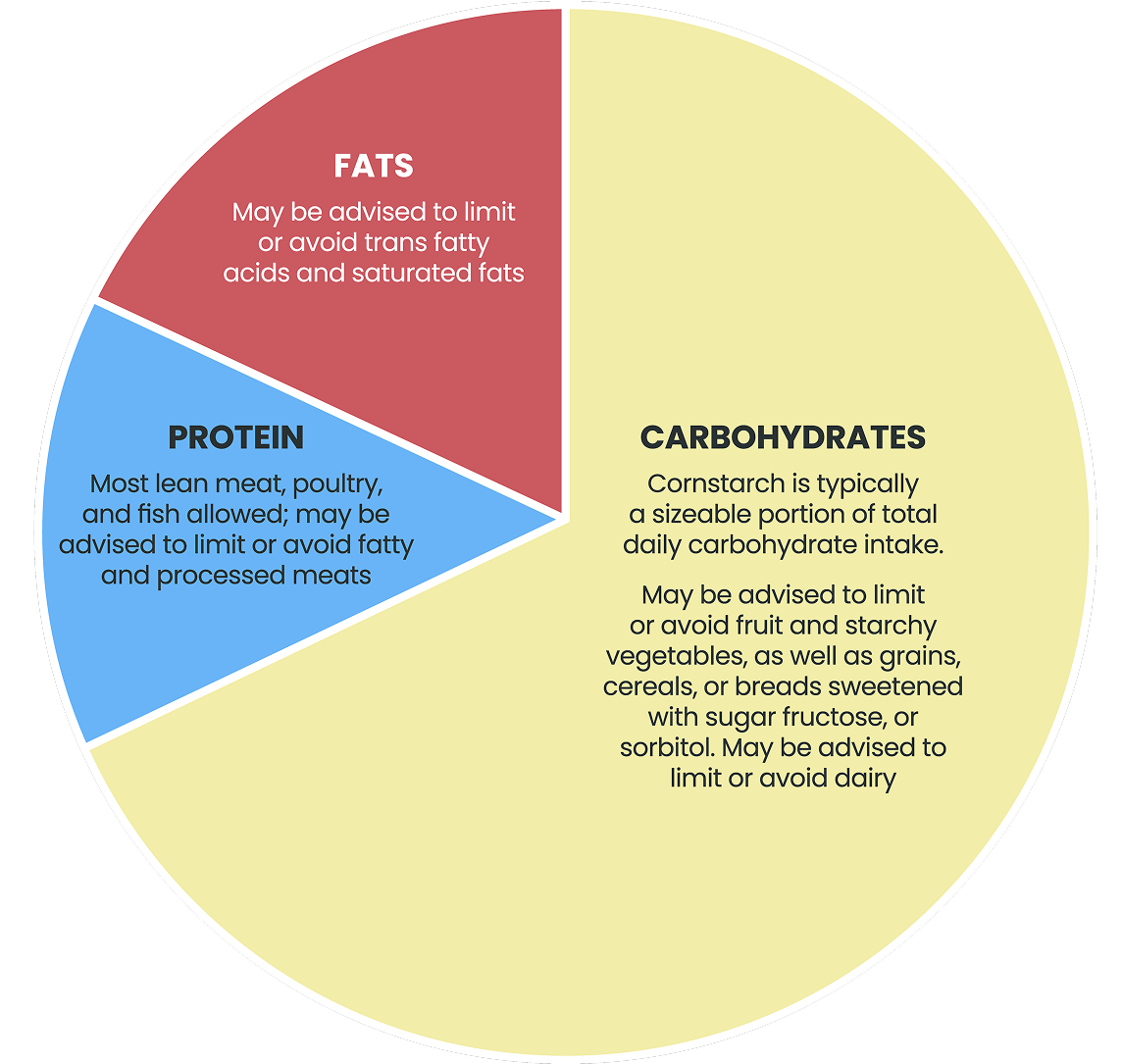
Disclaimer: For illustrative purposes only. Patients should work with their care team to develop an appropriate nutrition plan that meets their unique needs.
Abbreviation: GSDIa, glycogen storage disease type Ia.
References: 1. Kishnani PS, Austin SL, Abdenur JE, et al. Diagnosis
and management of glycogen storage disease type I: a practice guideline of the American College of Medical
Genetics and Genomics. Genet Med. 2014;16(11):e1. 2. Derks
TGJ, Rodriguez-Buritica DF, Ahmad A, et al. Glycogen storage disease type Ia: current management options,
burden and unmet need. Nutrients. 2021;13(11):3828. 3.
Correia CE, Bhattacharya K, Lee PJ, et al. Use of modified cornstarch therapy to extend fasting in glycogen
storage disease types Ia and Ib. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;88(5):1272-1276. 4. Kruger E, de Freitas HM, Ferrecchia I, Gaydon M, Lloyd A. People and families
affected by glycogen storage disease type Ia: an analysis of narrative accounts written by individuals
living with GSDIa and their caregivers. J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2025;12(1):120-128. 5. Bali DS, El-Gharbawy A, Austin S, et al. Glycogen storage disease
type I. 2006. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA):
University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024. Accessed June 27, 2025.